Rubber sheeting may improve the value of such sources and make them easier to compare to modern maps.
Rubber sheet transformation in gis.
An affine transformation can differentially scale the data skew it rotate it and translate it.
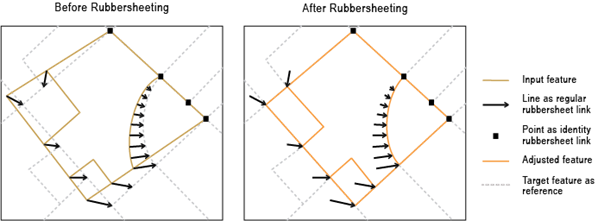
The input link features represent the regular links.
Affine similarity and projective.
Root mean square error measure of registration accuracy used during digitizing and coverage transformations.
Qgis is a free open source gis package.
By default arcmap supports three types of transformations.
X ax by c y dx ey f.
This drawback brings us to the idea of incorporating the historical maps into gis after rubber sheet transformation i e.
Click the spatial adjustment menu point to adjustment methods then click rubbersheet to set the adjustment method.
Rubber sheeting is a useful technique in historical gis where it is used to digitize and add old maps as feature layers in a modern gis.
The input point features represent identity links that hold source positions unmoved during the rubbersheeting process.
Click the general tab.
Used to control rubber sheeting and adjustment operations.
Qgis georeferencer plug in provides a number of transformation types including thin plate spline which enables full rubber sheeting.
Geometric distortions commonly occur in source maps.
Rubbersheeting makes spatial adjustments to align the input feature locations with more accurate target feature locations based on the specified rubbersheet links.
Cadcorp spatial information system software sis map modeller is offering a tool for rubbersheeting data layers.
Rubbersheeting is used to make small geometric adjustments in your data usually to align features with more accurate information.
You can press and hold the spacebar to temporarily turn off snapping as you create anchor points and draw displacement links or rubber sheet area polygons.
The graphic below illustrates the four possible changes.
Click rubbersheet for the adjustment method so you can set additional options for rubbersheeting.
Click the spatial adjustment menu and click options.
Click the adjustment methods drop down arrow and click rubbersheet.
Click the spatial adjustment menu and click options.
On the edit tab in the features group click modify.
Click the spatial adjustment menu point to adjustment methods then click a transformation method.
The affine transformation function is.
Click either the natural neighbor or linear method and click ok.
Rubber sheeting topological process of stretching or shrinking a subarea or portion of a map or image to fit in registration with selected control points.
Before aerial photography arrived most maps were highly inaccurate by modern standards.
Expand alignment and click transform.
The modify features pane appears.
They may be introduced by imperfect registration in map compilation lack of geodetic control in source data or a variety of other causes.